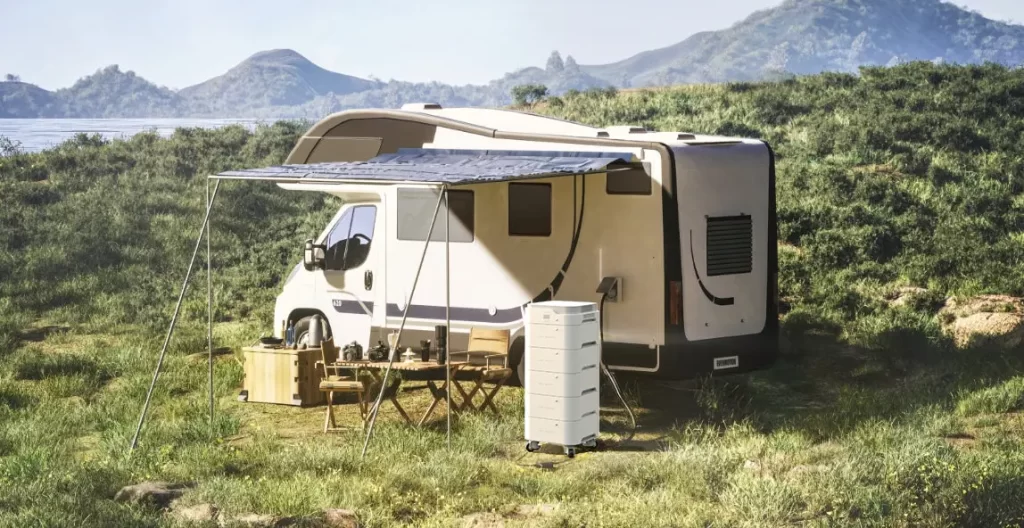
As the world increasingly leans towards sustainable and independent energy solutions, off-grid generator battery systems are gaining significant attention. These systems are essential for those who seek energy independence, live in remote locations, or wish to reduce their carbon footprint. This article delves into the intricacies of off-grid generator battery systems, exploring their components, benefits, and considerations for implementation.
What is an Off-Grid Generator Battery System?
An off-grid generator battery system is a self-sufficient energy solution that operates independently of the traditional electrical grid. It typically comprises a generator, a battery bank, inverters, and sometimes renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines. This system is designed to store energy generated by the generator or renewable sources in batteries, which can then be used to power homes, cabins, or other off-grid locations.
Key Components
- Generator:
- Function: Generates electricity, usually powered by diesel, gasoline, or propane.
- Role: Acts as a primary or backup power source, especially during periods when renewable energy generation is low.
- Battery Bank:
- Function: Stores the electricity generated by the generator or renewable sources.
- Types: Common types include lead-acid, lithium-ion, and nickel-cadmium batteries.
- Capacity: Determined by the total energy needs and the duration for which power is required without recharging.
- Inverter:
- Function: Converts the stored DC (direct current) power in the batteries to AC (alternating current) power, which is used by most household appliances.
- Types: Pure sine wave inverters are preferred for sensitive electronics, while modified sine wave inverters are more economical.
- Renewable Energy Sources (Optional but recommended):
- Solar Panels: Convert sunlight into electricity.
- Wind Turbines: Convert wind energy into electricity.
- Role: Reduce reliance on the generator, lower fuel costs, and promote sustainability.
Benefits of Off-Grid Generator Battery Systems
- Energy Independence:
- Complete autonomy from the electrical grid ensures a reliable power supply, especially in remote or disaster-prone areas.
- Environmental Impact:
- Utilizing renewable energy sources reduces carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
- Cost Savings:
- While the initial investment can be high, long-term savings are realized through reduced utility bills and fuel costs.
- Reliability:
- Battery storage ensures a continuous power supply even during generator downtime or renewable energy lulls.
- Scalability:
- Systems can be scaled according to energy needs, making them suitable for various applications from small cabins to large homes.
Considerations for Implementation
- Energy Assessment:
- Conduct a thorough energy audit to determine the total power requirements and appropriate system size.
- Budget:
- Consider the initial investment versus long-term savings. Quality components may have a higher upfront cost but offer better performance and longevity.
- Location:
- Assess the availability of renewable energy sources (solar, wind) and the practicality of installing such systems.
- Maintenance:
- Regular maintenance of generators, batteries, and renewable energy components is crucial for optimal performance and longevity.
- Regulations:
- Check local regulations and permits required for installing off-grid systems, especially renewable energy components.
Off-grid generator battery systems represent a viable solution for those seeking energy independence, sustainability, and reliability. By understanding the components, benefits, and considerations involved, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their energy needs and environmental goals. As technology advances and costs decrease, these systems will likely become more accessible and popular, contributing to a greener and more self-sufficient future.