As renewable energy becomes increasingly popular, many homeowners are turning to solar power systems to reduce their dependence on traditional utility companies. One of the most efficient and cost-effective options is a grid-tied solar system. In this guide, we will explore what a grid-tied solar system is, how it works, and how adding energy storage can provide continuous power during grid outages.
What is a Grid-Tied Solar System?
A grid-tied solar system, also known as an on-grid or grid-connected solar system, is designed to work in conjunction with the local utility grid. This type of system allows homeowners to generate their own electricity using solar panels while still being connected to the public electricity grid. The main components of a grid-tied solar system include:
- Solar Panels: These capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Inverter: Converts DC electricity from the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used by most household appliances.
- Net Metering: A billing mechanism that credits solar energy system owners for the electricity they add to the grid. When your system produces more electricity than you need, the excess is sent back to the grid, and you receive credits on your electricity bill.
- Utility Grid Connection: Ensures that any additional electricity needed beyond what your solar panels produce can be drawn from the grid.
Advantages of a Grid-Tied Solar System
- Cost Savings: Reduces electricity bills through net metering.
- Efficiency: Excess energy produced is not wasted but fed back into the grid.
- Lower Initial Investment: Generally, less expensive than off-grid systems because they don’t require batteries for storage.
Adding Energy Storage for Backup Power
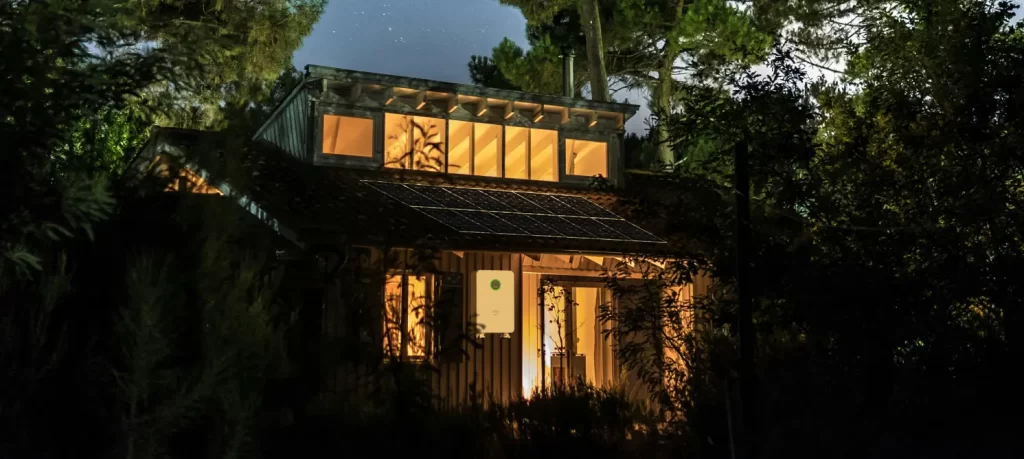

While grid-tied systems are highly efficient, they have a significant drawback: they do not provide power during a grid outage unless equipped with energy storage. By integrating battery storage into your grid-tied solar system, you can ensure continuous power supply even when the grid goes down. Here’s how you can achieve this:
Components of a Grid-Tied Solar System with Energy Storage
- Battery Bank: Stores excess energy generated by the solar panels for use during grid outages.
- Charge Controller: Manages the flow of electricity between the solar panels, battery bank, and inverter to prevent overcharging or deep discharging of batteries.
- Hybrid Inverter: Combines the functions of a standard inverter and a charge controller, allowing seamless switching between grid power, solar power, and battery power.
Steps to Integrate Energy Storage
- Assess Your Energy Needs: Determine how much backup power you need based on essential appliances and devices you want to keep running during an outage.
- Choose the Right Battery: Select a battery type that suits your needs. Common options include lead-acid, lithium-ion, and saltwater batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are generally preferred for their efficiency and longer lifespan.
- Install the Battery Bank: Work with a certified installer to properly integrate the battery bank with your existing grid-tied solar system.
- Configure the Hybrid Inverter: Ensure the hybrid inverter is correctly set up to manage the flow of electricity between the solar panels, battery, and grid.
- Test the System: Conduct thorough testing to make sure the system switches seamlessly to battery power during an outage and returns to grid power once the outage is resolved.
Benefits of Adding Energy Storage
- Uninterrupted Power Supply: Provides reliable power during grid outages, ensuring critical appliances remain operational.
- Energy Independence: Reduces reliance on the grid, offering greater control over your energy usage.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Optimizes the use of solar energy by storing excess production for later use.
Integrating a grid-tied solar system with energy storage offers the best of both worlds: cost savings and reliability. While the initial investment may be higher due to the addition of batteries and a hybrid inverter, the long-term benefits of uninterrupted power and increased energy independence make it a worthwhile consideration. Always consult with a professional installer to ensure your system is designed and configured to meet your specific needs. With the right setup, you can enjoy sustainable and reliable power for years to come.