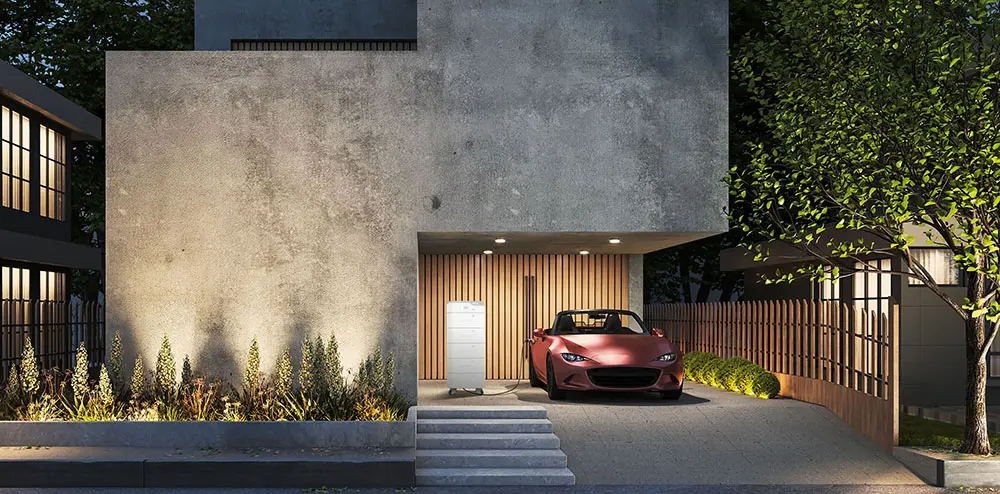
In an era where power outages can disrupt our daily lives, having a reliable home battery backup system is becoming increasingly important. Whether due to natural disasters, grid failures, or simply to ensure an uninterrupted power supply, a home battery backup can provide peace of mind. This guide will walk you through the essentials of creating your own DIY home battery backup system.
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the DIY aspect, it’s crucial to understand what a home battery backup system entails. Essentially, it consists of a battery bank that stores electricity, an inverter to convert the stored DC power into AC power, and a charge controller to manage the power flow. These components work together to ensure that your home has a steady power supply during outages.
Components Needed
Batteries
The heart of your backup system is the battery bank. There are several types of batteries to consider:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Affordable and widely used, but heavy and have a shorter lifespan.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: More expensive but lighter, longer-lasting, and more efficient.
- Nickel-Iron Batteries: Extremely durable and long-lasting, but less efficient and more expensive.
Inverter
An inverter is necessary to convert the DC power stored in the batteries to AC power, which is used by most household appliances. When choosing an inverter, make sure it matches the voltage of your battery bank and has enough capacity to handle your power needs.
Charge Controller
A charge controller regulates the power going into the batteries, preventing overcharging and prolonging battery life. There are two main types:
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): More affordable but less efficient.
- MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking): More expensive but significantly more efficient.
Battery Management System (BMS)
A BMS monitors and manages the individual cells within your battery bank, ensuring they operate safely and efficiently. This is particularly important for lithium-ion batteries.
Wiring and Safety Equipment
High-quality wiring, fuses, and circuit breakers are essential for safely connecting your components. Proper insulation and ventilation are also crucial to prevent overheating and potential hazards.
Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Determine Your Power Needs
Calculate your household’s power consumption to determine the size of the battery bank and inverter you’ll need. Make a list of essential appliances and their wattage, then estimate how long you need them to run during an outage.
Step 2: Choose and Purchase Components
Based on your power needs and budget, select the appropriate batteries, inverter, charge controller, and BMS. Don’t forget to buy high-quality wiring and safety equipment.
Step 3: Assemble the Battery Bank
Connect the batteries in series or parallel, depending on your voltage requirements. Ensure all connections are secure and well-insulated. If using lithium-ion batteries, install the BMS to monitor and manage the cells.
Step 4: Install the Inverter and Charge Controller
Mount the inverter and charge controller in a well-ventilated area close to the battery bank. Connect the batteries to the charge controller, and then connect the charge controller to the inverter.
Step 5: Connect to Your Home’s Electrical System
For safety reasons, it’s recommended to have a licensed electrician connect your battery backup system to your home’s electrical panel. This ensures compliance with local codes and prevents potential hazards.
Step 6: Test the System
Before relying on your new battery backup, thoroughly test the system to ensure everything is functioning correctly. Simulate a power outage to see how well the system handles your household’s power needs.
Maintenance and Safety Tips
- Regularly Check Connections: Ensure all connections are tight and free of corrosion.
- Monitor Battery Health: Periodically check the voltage and capacity of your batteries.
- Keep It Cool: Ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest safety standards and best practices for battery storage and handling.
Building your own DIY home battery backup system can be a rewarding and practical project. By understanding the components, carefully planning, and following safety guidelines, you can create a reliable power source that keeps your home running smoothly during outages. Whether you opt for lead-acid, lithium-ion, or nickel-iron batteries, the key is to ensure that your system is well-designed and properly maintained. With a little effort and investment, you can enjoy the peace of mind that comes with having a dependable home battery backup.