In today’s fast-paced and technology-driven world, the continuous availability of electricity is paramount. Whether it’s a residential home, a bustling office, or a critical healthcare facility, power outages can cause significant disruptions and even pose serious risks. This is where backup power inverters come into play, offering a reliable solution to keep essential systems running smoothly during unexpected power interruptions.
What is a Backup Power Inverter?
A backup power inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) from a battery or other power source into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form of electricity used by most household appliances and electronic devices. Unlike generators, which produce electricity through mechanical means, inverters rely on stored energy, typically from batteries, to provide power. This makes them a cleaner and quieter alternative for emergency power needs.
How Do Backup Power Inverters Work?
The primary function of a backup power inverter is to ensure that electrical devices remain operational during a power outage. When the main power supply is interrupted, the inverter automatically switches to battery power, converting the stored DC into usable AC. This seamless transition ensures that critical systems, such as medical equipment, computers, and communication devices, experience minimal downtime.
Types of Backup Power Inverters
- Pure Sine Wave Inverters: These inverters produce a smooth and consistent wave of electricity, similar to that provided by the utility grid. They are ideal for sensitive electronics and equipment that require a stable power supply.
- Modified Sine Wave Inverters: These inverters generate a stepped approximation of a sine wave. While they are more affordable, they may not be suitable for all types of equipment, particularly those with sensitive electronics.
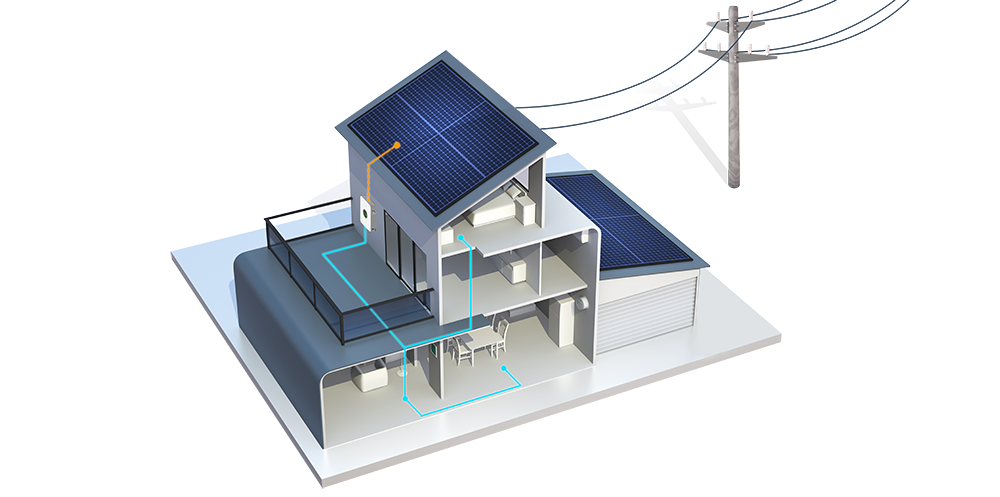
- Grid-Tie Inverters: These inverters work in conjunction with the utility grid, allowing for the seamless integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels. They can feed excess power back into the grid, providing an environmentally friendly backup solution.
Benefits of Using Backup Power Inverters
- Reliability: Backup power inverters provide a dependable source of electricity during outages, ensuring that essential systems remain operational.
- Versatility: Inverters can be used in a variety of settings, from homes and offices to remote locations and emergency situations.
- Environmentally Friendly: Unlike traditional generators, inverters produce no emissions and operate quietly, making them a greener alternative.
- Cost-Effective: While the initial investment in a backup power inverter system may be higher than a generator, the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance can make it a more economical choice.
- Ease of Use: Modern inverters are designed for user-friendly operation, with automatic switching and monitoring features that require minimal intervention.
Applications of Backup Power Inverters
Backup power inverters are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Residential: Ensuring that home appliances, security systems, and communication devices remain functional during power outages.
- Commercial: Keeping critical business operations, such as servers, point-of-sale systems, and lighting, running smoothly.
- Healthcare: Providing uninterrupted power to life-saving medical equipment and systems.
- Telecommunications: Maintaining the functionality of communication networks and data centers.
- Renewable Energy: Integrating with solar panels and other renewable energy sources to provide a sustainable backup power solution.
In an era where uninterrupted power is crucial, backup power inverters offer a reliable, versatile, and environmentally friendly solution. Whether for residential, commercial, or industrial use, these devices ensure that essential systems remain operational during power outages, providing peace of mind and continuity in our daily lives. Investing in a backup power inverter is not just a precaution; it’s a proactive step towards safeguarding against the uncertainties of power supply disruptions.