Portable power stations work by storing electrical energy in a built-in rechargeable battery, which can then be used to power various devices. Here’s a brief overview of the process:
- Charging the Battery: The battery can be charged through multiple methods, such as:
- AC Wall Outlet: Plugging into a household electrical outlet.
- Solar Panels: Using solar panels to harness solar energy.
- Car Charger: Connecting to a car’s 12V DC outlet.
- Storing Energy: Once charged, the battery stores the electrical energy as Direct Current (DC) power.
- Inverting Power: An inverter within the power station converts the stored DC power into Alternating Current (AC) power, which is used by most household appliances and electronic devices.
- Powering Devices: The power station features multiple output ports, including AC outlets, DC carports, USB-A, and USB-C ports. You can connect your devices to these ports to power or charge them.
- Managing Power: The device manages the energy flow to ensure each connected device receives the appropriate amount of power, often displaying battery levels and power usage on an LCD or LED screen.
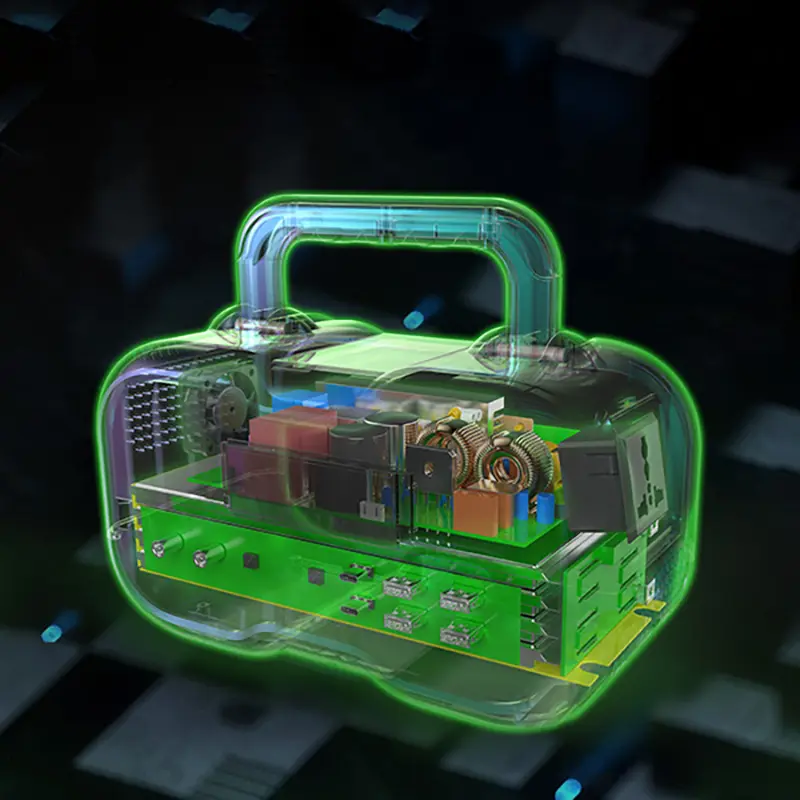

In summary, portable power stations work by charging a battery from various sources, storing the energy, converting it as needed, and then distributing it to connected devices through multiple output ports.